USB Flash Drive Memory Chip Swap for Data Recovery
One unconventional method that has gained attention among data recovery professionals is the USB flash drive memory chip swap technique. This technique involves physically swapping the memory chips from a malfunctioning flash drive onto a working one to retrieve lost data. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of this procedure, its feasibility, risks, and ethical considerations.
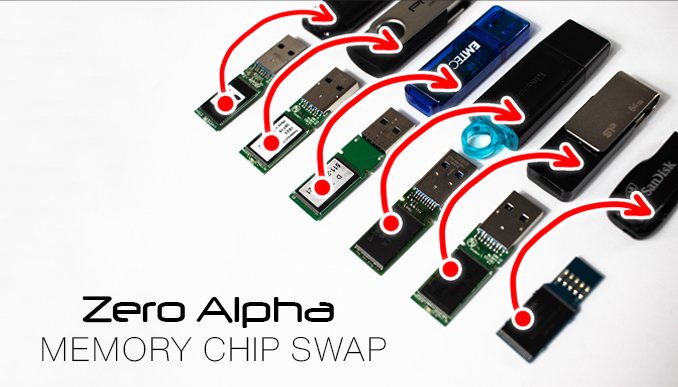
Understanding the Memory Chip Swap Technique
USB flash drives store data on memory chips, which are essentially integrated circuits capable of storing binary data in the form of electrical charges. When a flash drive fails due to physical damage, such as a broken connector or corrupted firmware, the memory chips themselves may remain intact. The memory chip swap technique capitalizes on this aspect by transferring the memory chips from the damaged flash drive onto a functional one with identical specifications.
Feasibility and Challenges
The feasibility of this technique largely depends on several factors:
-
Matching Specifications: For a successful memory chip swap, the donor and recipient flash drives must share identical specifications, including the controller, NAND type, capacity, and interface.
-
Soldering Expertise: This procedure requires advanced soldering skills, as the memory chips are delicate and sensitive to heat. Any damage caused during the soldering process could exacerbate data loss.
-
Firmware Compatibility: The firmware of the recipient flash drive needs to be compatible with the memory chips being swapped. Mismatches could lead to data corruption or device failure.
-
Data Encryption: If the data on the flash drive is encrypted, the memory chip swap alone won't recover the data, as the decryption key resides in the flash drive's original hardware. Decrypting the data may require additional steps.
Risks Involved
Undertaking a memory chip swap for data recovery poses significant risks:
-
Data Loss: Mishandling the delicate memory chips during the swap can lead to further data loss, rendering the recovery attempt futile.
-
Permanent Damage: Incorrect soldering or manipulation can permanently damage both the donor and recipient flash drives.
-
Legal and Ethical Concerns: Swapping memory chips raises concerns about ownership and unauthorized access to data. Recovering data without proper authorization might breach privacy regulations or intellectual property rights.
Professional Expertise and Ethical Considerations
Due to the complexity and risks associated with the memory chip swap technique, it is strongly recommended that only experienced professionals with a thorough understanding of flash drive architecture and soldering techniques attempt this procedure. Additionally, ethical considerations play a vital role. Data recovery professionals must adhere to legal and ethical guidelines, obtain proper authorization from device owners, and ensure that no confidential or sensitive data is compromised during the recovery process.
Alternatives to Consider
Before attempting a memory chip swap, it's crucial to explore less invasive data recovery methods, such as software-based solutions, contacting professional data recovery services, or seeking manufacturer support if the flash drive is under warranty.
Conclusion
The USB flash drive memory chip swap technique presents a compelling yet risky method for data recovery. While it holds potential for retrieving valuable information from damaged flash drives, its technical complexity, potential risks, and ethical concerns cannot be ignored. Before considering this approach, individuals and professionals must thoroughly assess the feasibility, weigh the risks, and explore alternative recovery options to ensure the best possible outcome for data retrieval.